Cloud Security Best Practices: How to Protect Your Data in the Cloud
Cloud data security has been a short-term necessity instead of a long-term goal among enterprises using cloud services, especially those in hybrid or multi-cloud environments. This blog will highlight thirteen recommended cloud security best practices organizations can implement throughout their cloud adoption process to keep their environments secure from cyberattacks.
What is Cloud Data Security? A Quick Overview
Cloud data security is the process of protecting data and other digital information assets from security threats, human error, and insider threats. It uses technologies, systems, and processes to keep your data private and still accessible to those who need it in cloud-based environments.
The basic principles of information security and data governance—data confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility (known as the CIA triangle)—also apply to the cloud.

These principles apply notwithstanding the following: Which cloud model does the company adopt—public, private, hybrid, or local cloud? Which cloud computing units does the organization use—Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), or Function-as-a-Service ( FaaS )?
Organizations need to consider data security at all stages of the cloud computing and data lifecycle, from designing, deploying, or migrating systems and systems to managing cloud environments.
What Are Some of The Challenges of Cloud Security?
As businesses increasingly embrace cloud computing, a spectrum of risks emerges, demanding a vigilant approach to safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining robust cybersecurity measures. Let’s delve into some of the common cloud data security risks that organizations face, including.
1. Access Management and Shadow IT
While enterprises may be able to successfully monitor and restrict access to internal systems, enforcing these same restrictions can be challenging in cloud environments. This can be a risk for organizations that do not use their own device (BYOD) policies and allow unconstrained access to cloud services from any device or geolocation.

2. Multitenancy Offering
Public cloud environments have multiple types of client infrastructure under one umbrella, so it’s possible that malicious attackers could compromise your hosted services while you set your sights on other projects. This emphasizes the importance of continuous surveillance, proactive safety measures, and appropriate separation of resources.
For example, using network segmentation can add additional security by isolating critical services and the potential impact of a security breach. These techniques are critical for mitigating threats and protecting the integrity of the entire cloud environment.
3. Misconfiguration
In 2019, 86% of records breaches were from unstructured assets, making unintentional insider a major issue for cloud computing environments. Misconfiguration can include leaving default administrative passwords in place or not setting appropriate privacy settings.

4. Lack of Visibility
It’s easy to see how your data is accessed and by whom, as many cloud services are accessible outside of corporate networks and through third parties. Moreover, addressing the Lack of Visibility challenge necessitates a proactive stance in developing comprehensive audit trails and real-time monitoring.
By doing so, organizations can not only enhance their ability to trace data access but also expedite the identification and response to potential security breaches, thereby reinforcing the integrity of their cloud environments.
5. Compliance
Monitoring compliance is often confusing for enterprises using public or hybrid cloud deployments. Both data privacy and security accountability still rests with the company, and heavy reliance on third-party solutions to handle this phase can create significant compliance issues.
According to Snyk’s report, 80% of organizations experienced a notable security incident linked to their cloud infrastructure in the previous year.
Certainly! Here’s the table highlighting the frequency of cloud attacks:

This table provides a breakdown of the reported percentages for various cloud security incidents.
| Cloud Security Incidents | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Total Incidents Reported | 80% |
| Cloud Data Breach | 33% |
| Cloud Data Leak | 28% |
| Environment Intrusion | 27% |
| Cryptomining | 23% |
| Serious Compliance Violation | 25% |
| Failed Audit | 15% |
| System Downtime (Misconfiguration) | 34% |
What are the Best Practices for Security Data in the Cloud?
Let’s dive deep into the key practices for securing your data in the cloud. From encryption protocols to access management, explore actionable insights and best practices to bolster your cloud security strategy.
1. Choose a Reliable Cloud Service Provider
Choosing a reputable and trusted cloud service provider (CSP) is important to ensure the security of your data. Conduct a thorough investigation and consider things like data privacy, data center security, certificate of compliance, and past security issues. Choose a CSP that meets your organization’s security needs.
2. Understand Cloud Security Rules
Unlike private data centers, where the organization is fully in charge of security, the public cloud adds complexity and sometimes some confusion. Ultimately, the cloud customer is responsible for cloud security, but cloud service providers assume some security responsibility, a system called shared responsibility, for example, large IaaS and PaaS providers, such as AWS web services and Microsoft Azure, provide documentation to define services in different operating conditions.
Companies considering cloud vendors should review these general security rules to minimize miscommunications and misunderstandings so that critical security measures and incidents can go unnoticed, but as long as the customer does their part, such as using encryption and properly configuring communications and systems, generally, data will do get secure.
3. Ensure a Strong Cloud Perimeter
In cloud networks driven by software-defined networking (SDN), prioritize security through strategic measures. Segment workloads into distinct virtual networks, control incoming traffic with firewalls and implement a web application firewall (WAF) for added defense against specific application security risks. Integrate DDoS protection tools for organized attack prevention.
Strengthen your network perimeter with a robust firewall, be it cloud-native or a third-party tool, and consider supplementary measures like intrusion detection or prevention systems for comprehensive cloud security.
4. Get a Visible Level of Security
As the cloud computing platforms expand, the chances of the breach going unreported increase. Having the right tools will help you determine your most needed level of security so you can address security quickly.
All major cloud computing platforms have an advanced/premium tier of native CSPM solutions that can provide capabilities such as data mining detection, incident threat detection, IAM account hijacking, and cryptomining, to name a few, but note that these features tend to be them the cloud only platform. Including special tools to determine the security level for hybrid or multi-cloud deployments is recommended.
5. Vulnerability Assessment and Remediation
To protect your business, you can access real-time vulnerability scanning and prevention services against virus and malware attacks. The service must be able to support deployed workloads on VMs as well as containers. Consider a vulnerability management solution that can continuously look for business vulnerabilities, collect reports, and present the results in a dashboard, resolving the issues automatically where possible.
6. Misconfiguration
Successful cloud business access is often due to service misconfiguration or manual configuration errors. A cloud security posture management (CSPM) solution should be integrated into your architecture to check for malfunctions that can get into your cloud deployment. CSPM solutions add value by evaluating your deployments against best practice guidelines.
These may be organization-specific standards or align with priority security and compliance standards. A secure score is provided that reflects the current security status of your entire business in the cloud, whereas a positive security score indicates that you have deployed a secure cloud. These tools will also indicate if practices deviate from what is intended to enable customers to make the necessary corrections.
7. Implement Cloud Security Measures
A cloud security strategy is defined to implement organization-wide constraints to ensure security. For example, use public IPs to limit business processes, manage east-west traffic, or implement container business traffic management. Implementation methods vary among service providers. In Azure, customers can use Azure policies, while in GCP, this can be done using organizational policies. A security policy’s benefit is enforcing compliance across the board in cloud deployments.
8. Implement Identity & Access Management
When it comes to your cloud business, control plane security is important because it holds the state keys. You will need to use your cloud platform’s basic identity and access management services to implement usage-based, fine-grained access control of cloud resources.
Cloud platforms also provide tools for seamless integration with on-premises solutions such as Active Directory and cloud-native Identity and Access Management (IAM) services, thereby providing a seamless user experience. Single sign-on (SSO) for cloud hosting workloads ) can be provided. When it comes to IAM controls, the rule of thumb is to follow the principle of least privilege, which means that critical users can access the data and cloud resources they need to perform their jobs.
9. Implement a Cybersecurity Training Program
There are great tools to defend the data cloud against various adversaries, but many security leaders have realized something: it is better to be proactive about cybersecurity. Implementing a comprehensive security training program for employees is a great starting point for embedding cybersecurity into the organizational culture, making it a priority for employees and other stakeholders.
Ensure that the program uses common adversaries in your industry and how they attack themselves. Additionally, include specific training designed to detect phishing attempts, as phishing is one of the most common ways for hackers to gain unauthorized access to company networks and potentially sensitive information one of the most common ways hackers obtain unauthorized access to an organization’s network and potentially sensitive information.
10. Meet IT Compliance Requirements
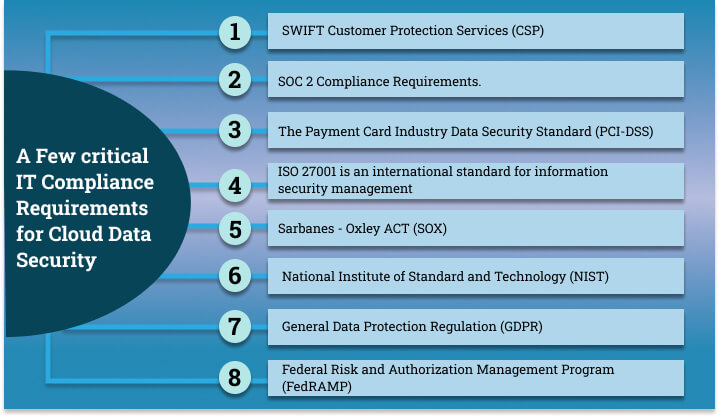
In order to meet IT compliance requirements, you must first define the standards that apply to your business and what your organization must meet. For example, the following SWIFT Customer Protection Service (CSP) requirements are mandatory for any financial institution that uses SWIFT services.
Similarly, any organization that stores customer data in the cloud must follow SOC 2 compliance requirements. To make it easier to identify your organization’s needs, consider hiring a Data Protection Officer (DPO) who will provide you with sophisticated knowledge of cybersecurity and IT compliance.
As with any product, service, or process, data cloud security solutions and strategies must have the needs of the cloud and data compliance in mind. Compliant means it meets the standards set by law and regulation to ensure consumer protection.
11. Backup and Disaster Recovery Options
Implementing robust backup and disaster recovery strategies ensures that you can quickly restore your system and data in the event of an incident. Regularly back up critical data and test the recovery process to ensure it works properly. Consider using a cloud-based backup solution for additional redundancy and flexibility.
12. Conduct Regular Safety Audits
Regular cloud security audits are essential to identify and address vulnerabilities in your cloud environment. Perform penetration testing and vulnerability scanning to identify weaknesses in your systems. Review and regularly update security policies and procedures based on findings to improve your overall security posture.
13. Wrapping Up
In the digital age, cloud security is of utmost importance to protect sensitive data from potential threats. You can maintain stable and secure cloud computing platforms with these best practices. Remember to stay vigilant, adapt to emerging threats, and update your cloud computing infrastructure security on a regular basis to stay one step ahead of cybercriminals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What do you mean by database security?
Database security refers to the strategies to be used to protect databases from unauthorized access, data breaches, and malicious activity. This database uses a variety of tools, policies, and procedures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data stored.
Why is database testing important?
Database testing is essential to ensure the accuracy, reliability, and functionality of the database system. It helps identify and improve issues related to data integrity, data consistency, and system performance. Thorough testing ensures that the database works as intended, reducing the risk of bugs and vulnerabilities in real-world deployments.
How do you secure your database server?
A multi-tiered approach is used to connect to the database server. This includes setting up strong authentication and authorization controls, logging sensitive data, implementing routine security measures, monitoring database activity for anomalies, and security regular inspections in addition to adding additional protection by physically attacking the server.
What are database security testing methods?
In database security testing, various techniques are used to assess the robustness of a database system. This includes vulnerability analysis to identify potential vulnerabilities, penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks, and monitoring database systems to ensure compliance with best security practices. Database operations monitoring and routine inspections contribute to a comprehensive safety testing program.
How does encryption contribute to database security?
Encryption plays an important role in database security by converting sensitive data into unreadable ciphertext. This ensures that the data remains undecipherable without a valid decryption key, even if it is deciphered by an unauthorized user. Using encryption at rest and on the move adds an extra layer of security, protecting the confidentiality of sensitive information stored in the database.
